Figure 2 Generalized life cycle for American and Asian horseshoe crabs showing the approximate size of eggs and larvae and the dura-tion of each life stage which vary by species and are detailed in Tables 14 and associated citations. The Atlantic horseshow crabs usual method of locomotion is walking along the sea bed.
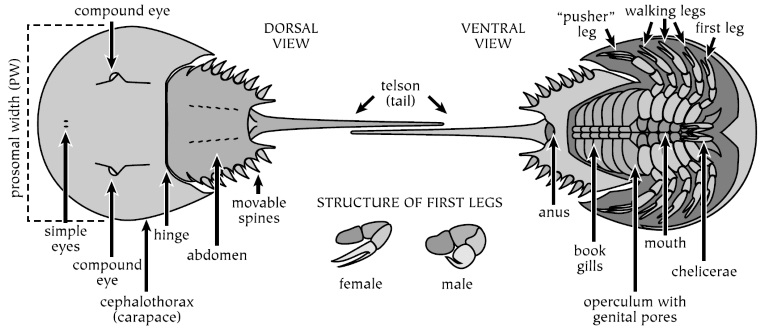
Students use information from the Student Master the Background information sheet and the clues on the horseshoe crab diagram sheets to label the diagrams with the 16 body parts listed on the Student Master.
Horseshoe crab life cycle diagram. Therefore the lifespan of horseshoe crabs may be 17 to 19 years in the northern part of their range accepting the estimate of 9 to 11 years to reach sexual maturity Shuster 1950. Like many animals horseshoe crabs exhibit sexual dimorphism. Once horseshoe crabs are ten years old they are mature and therefore a breeding adult.
The life cycle of the horseshoe crab looks like this. Lifecycle of the Horseshoe Crab. Scroll over the timeline below for a quick look at the horseshoe crabss life stages.
Juvenile horseshoe crabs generally spend their first and second summer on the intertidal flats feeding before the daytime low tide and burrowing in the sand for the rest of the day. The shell splits along the perimeter rim of the prosoma and allows the horseshoe crab to emerge. The horseshoe crab increases in size by a rapid uptake of water.
Most studies have concluded that there are at least 18 growth stages in the horseshoe crab lifecycle that encompass various stages of embryo larvae juvenile and adult. The horseshoe cabs spawns at high tide when the water is warmer than about 60F usually between spring and fall. The second pair of legs on a horseshoe crab are called the pedipalps.
She will lay as many as 90000 eggs a year but only lay 20000 eggs with one mate. An average egg takes 14 days to hatch from conception to birth. When it hatches it will start its life.
The horseshoe crab typically lives 20 years. July 20 2011 100 pm. Southwest 15 mph a gentle breeze wavelets crests break on the water.
The horseshoe crab a living fossil over 450 million years old continues to fascinate people and scientists alike. Most children fear this gentle creature with its hard helmet-shaped shell and. Life Cycle and Reproduction Horseshoe crabs can grow to two feet long and live up to 25 years.
In warmer waters within their geographic range they remain active all year but in cooler northern regions the crabs burrow into the mud and become inactive during the winter. Horseshoe crabs reach adulthood at nine to twelve years old. Horseshoe crabs go through 16 or 17 molts during their development.
At around 10 years of age horseshoe crabs reach adulthood. They are ready to start breeding and will migrate to coastal beaches in the spring. A horseshoe crab can live for more than 20 years.
After hatching horseshoe crabs spend their first few years of life on the tidal flats and move out farther from shore as they get older. Adults spend the winter in deep bay waters and off-shore areas. As spring approaches the crabs move en masse toward the beaches to prepare for spawning.
Since horseshoe crabs have a hard shell they must molt to grow. Check out our channel FunScienceDemos. American horseshoe crabs Limulus polyphemus have 10 eyesThey have two large lateral compound eyes each containing about 1000 clusters of photoreceptors or ommatidia.
A small lens within each ommatidium focuses light from a small patch of visual space onto each photoreceptor cluster which transmits information about local changes in light intensity to the brain through a nerve fiber. About This Quiz Worksheet. Complete the quiz and worksheet to see how familiar you are with horseshoe crabs.
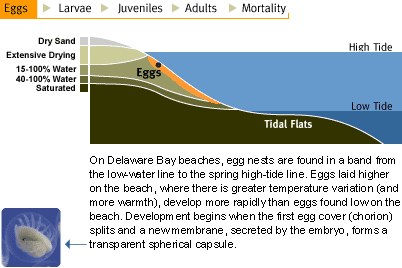
Quiz topics include the life cycle for this type of crab and how old they must be. Life CycleReproduction EggLarvae Stage Horseshoe crab eggs are buried higher up on sandy beaches in nests made by the female horseshoes. Temperatures vary here in the moist sand.
Each nest normally contain approximately 4000 eggs. An eggs size can be compared to a. Thus the horseshoe crab is constantly threatened with infection due to its environment.
The horseshoe crab lacks an immune system. It does contain a number of compounds that will bind to and inactivate bacteria fungi and viruses. It is one of the marvels of evolution that the horseshoe crab uses endotoxin as a signal for wound occurrence and as an extremely effective defense against.
Figure 2 Generalized life cycle for American and Asian horseshoe crabs showing the approximate size of eggs and larvae and the dura-tion of each life stage which vary by species and are detailed in Tables 14 and associated citations. Polyphemus are shown as an example of each life stage including preserved develop-. Four horseshoe crab diagrams until it is time for them to do the activity in class.
Students use information from the Student Master the Background information sheet and the clues on the horseshoe crab diagram sheets to label the diagrams with the 16 body parts listed on the Student Master. The horseshoe crab is able to sense smell using a small organ located on the triangle-shaped area on the underside of its body. The Atlantic horseshow crabs usual method of locomotion is walking along the sea bed.
The horseshoe crab is also able to swim which it does upside-down propelling itself along with its legs.